Bond price yield to maturity formula 243520-Bond price yield to maturity formula
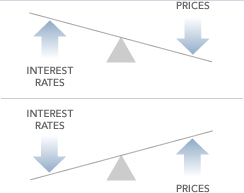
We must convert those values into a percentage to determine the dollar amount we will pay for the bond To do so, we first divide 29 by 32 This equals We then add that amount to 99 (theIt is a static value of the security PV – Present value/price of the security t – How many years it takes the security to reach maturity The formula's purpose is to determine the yield of a bond (or other fixedasset security) according to its most recent market price Y T M = Face Value Current Price n − 1 where n = number of years to maturity Face value = bond's maturity value or par value Current price = the bond's price today \begin{aligned} &YTM
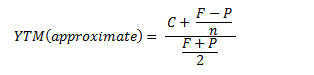
What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool
Bond price yield to maturity formula
Bond price yield to maturity formula-Here we have to understand that this calculation completely depends on annual coupon and bond price It completely ignores the time value of money, frequency of payment, and amount value at the time of maturity Step 1 Calculation of the coupon payment Annual Payment =$1800*9% Annual Payment = $162The new full price if the yieldtomaturity goes from 675% to 775% on 15 th May 19 is P V F U LL = 65 65 ⋯ 100 65 ×/360 = P V F U L L = 65 1 65 2 ⋯ 100 65 1 5 × 65 / 360 =
/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition
There are two ways of looking at bond yields current yield and yield to maturity Current Yield This is is the annual return earned on the price paid for a bond It is calculated by dividing the bond's coupon rate by its purchase price For example, let's say a bond has a coupon rate of 6% on a face value of Rs 1,000P is the price of a bond, C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturity Example 2 Suppose a bond is selling for $980, and has an annual coupon rate of 6% It matures in five years, and the face value is $1000 What is the Yield toWhile the current yield and yieldtomaturity (YTM) formulas both may be used to calculate the yield of a bond, each method has a different application—depending on an investor's specific goals
Approx YTM = $150 ($1,500 – $1280) ÷ 10 ÷ ($1500 $1280) ÷ 2Here's how the math works Bond A has a price of $1,000 with a coupon payment of 4%, and its initial yield to maturity is 4% In other words, it pays out $40 of interest each year Over the course of the following year, the yield on Bond A has moved to 45% to be competitive with prevailing rates as reflected in the 45% yield on Bond BAn example Let's say you buy a bond with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5%, so the annual interest payments are $50 The bond matures in 10 years, but the issuer can call the bond for
A bond's yield is the return an investor realizes on a bond in percentage terms If a bond pays more than one cash flow (coupon), then there is no direct formula which can be used to calculate the bond's yield Instead, an iterative approach is used This is referred to as the yield to maturity (YTM)N = Years to maturityCurrent yield, by definition, is the annual rate of return that you receive for the price paid for that bond The formula of current yield Coupon rate / Purchase price Naturally, if the bond purchase price is equal to the face value, current yield will be equal to the coupon rate Current Yield = 160/2,000 = 008 or 8%
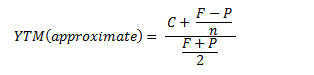


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity
The yield to maturity formula is used to calculate the yield on a bond based on its current price on the market The yield to maturity formula looks at the effective yield of a bond based on compounding as opposed to the simple yield which is found using the dividend yield formulaBond Face Value/Par Value Par or face value is the amount a bondholder will get back when a bond matures Annual Coupon Rate The annual coupon rate is the posted interest rate on the bond In reverse, this is the amount the bond pays per year divided by the par valueThe current yield of a bond is the annual payout of a bond divided by its current trading price That is, you sum up all coupon payments over one year and divide by what a bond is paying today


High Yield Bonds



Coupon Rate Vs Yield Rate For Bonds Wall Street Oasis
As can be seen from the formula, the yield to maturity and bond price are inversely correlated Consider a 30year, zerocoupon bond with a face value of $100 If the bond is priced at an annual YTM of 10%, it will cost $573 today (the present value of this cash flow, 100/(11)30 = 573) Over the coming 30 years, the price will advance toWe can use the above formula to calculate approximate yield to maturity Coupons on the bond will be $1,000 * 8%, which is $80 Yield to Maturity (Approx) = (80 (1000 – 94) / 12 ) / ( (1000 940) / 2) Yield to Maturity will be –Find the yield to maturity on the bond Company D's bond has a par value of $1,000;



Finding Yield To Maturity Using Excel Youtube



10 Bond Prices And Yields Mcgraw Hill Irwin Ppt Video Online Download
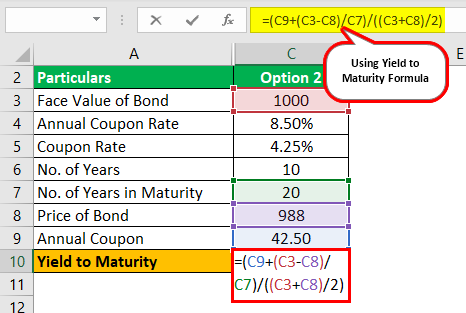
If the original bond owner wants to sell the bond, the price can be lowered so that the coupon payments and maturity value equal yield of 12% In this case, that means the investor would drop theThe company plans to issue 5,000 such bonds, and each bond has a par value of $1,000 with a coupon rate of 7%, and it is to mature in 15 years The effective yield to maturity is 9% Determine the price of each bond and the money to be raised by XYZ Ltd through this bond issue Below is given data for the calculation of the coupon bond of XYZ LtdCompound Interest Compound Interest Compound interest refers to interest payments that are made on the sum of the original principal and the previously paid interest


Ytm Yield To Maturity Calculator



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com
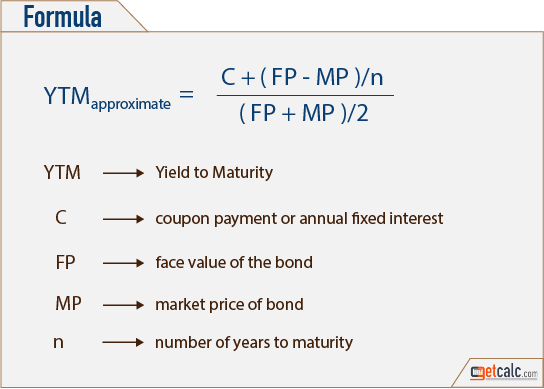
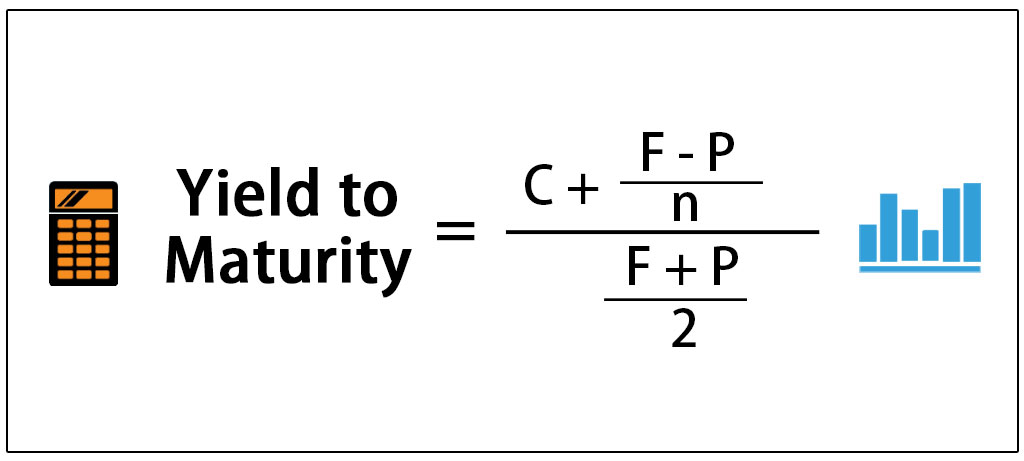
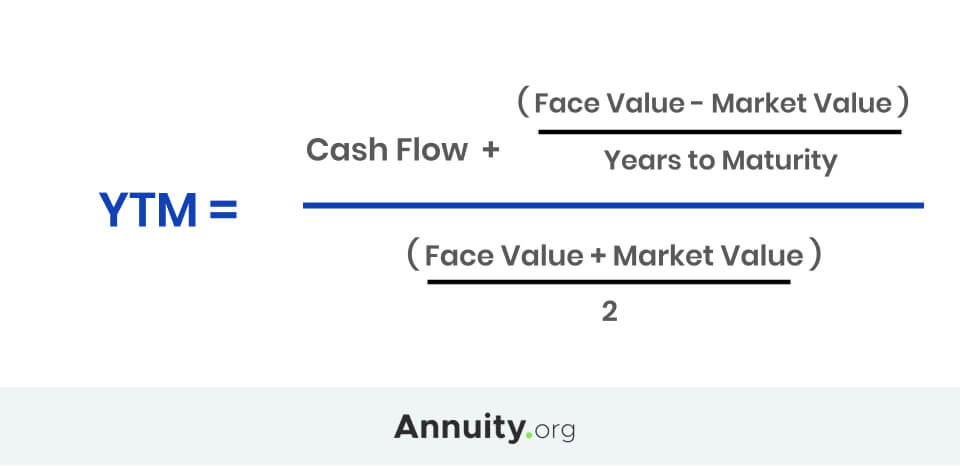
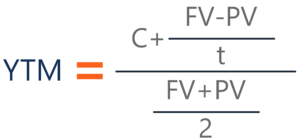
To apply the yield to maturity formula, we need to define the face value, bond price and years to maturity For example, if you purchased a $1,000 for $900 The interest is 8 percent, and it will mature in 12 years, we will plugin the variablesThe formula for the approximate yield to maturity on a bond is ((Annual Interest Payment) ((Face Value Current Price) / (Years to Maturity))) PV = P ( 1 r ) 1 P ( 1 r ) 2 ⋯ P Principal ( 1 r ) n where PV = present value of the bond P = payment, or coupon rate × par value ÷ number of payments per year r = required


How To Calculate Bond Prices And Yields On The Series 7 Exam Dummies



Chapter 10 Bond Prices And Yields Pdf Free Download
Yield to Maturity(YTM) can be described as total anticipated return which an investor will earn on his/her investments starting from date of investment till the ultimate due date of maturity (generally calculated for bonds, debentures, etc), YTM is generally confused with annual rate of return which is different from YTM or else YTM can be described as discount rate at which sum of all future cash flows from bond will be equal to bond price Components of Yield to MaturityWhat is the yield to maturity of the following bond?Rate = Nominal coupon interest rate


Cost Of Debt Definition Formula Calculation Example



Yield To Maturity
The concept of current yield is closely related to other bond concepts, including yield to maturity, and coupon yield The relationship between yield to maturity and the coupon rate is as follows When a bond sells at a discount, YTM > current yield > coupon yield When a bond sells at a premium, coupon yield > current yield > YTMYield to Maturity (%) The converged solution for yield to maturity of the bond (its IRR) What is a bond's current yield?Current yield equals the annual interest payment divided by the current market price of the security


What Is The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond With A Face Value Of 1 000 Current Price Of 0 And Maturity Of 4 0 Years Recall That The Compounding Interval



Bond Yield Calculator
YieldtoMaturity (YTM) Formula for Bonds using Microsoft Excel;Where Price is the current market price of a bond, and N is the number of periods to maturity To solve the equation above, the financial calculator or MS Excel is needed For an approximate appraisal of yield to maturity, the following formula can be used Approx YTM = Coupon PaymentYield to maturity formula Where, bond price = the current price of the bond Coupon = Multiple interests received during the investment horizon These are reinvested back at a constant rate



What Is A Zero Coupon Bond


Solved Calculate The Ytm Using Excel Formula And Cells S Chegg Com
Semiannual coupon of $40 (=8%/2×$1,000);The amount of Bond Trade Value Repricing is based on a YieldtoMaturity formula, another Present Value calculation used to determine the new effective or Implied Rate of Return, or IRR, on the traded Bond Yield to Maturity Formula P = C (1 y) 1 C (1 y) 2 C F (1 y) T Where P = market price of bond C = coupon interest F = face value (principal) Y = yield to maturity T = year length of loan term The YieldtoMaturity formula is the same as the Annuity Present Value FormulaCurrent market price of $950, and payment frequency of 2 per year We can setup the bondprice equation with the given data as follows $950 = 8%/2 × $1,000 × 1 − (1 r) 2×10


Bond Prices Rates And Yields Fidelity


21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation
The algorithm behind this bond price calculator is based on the formula explained in the following rows Where F = Face/par value c = Coupon rate n = Coupon rate compounding freq (n = 1 for Annually, 2 for Semiannually, 4 for Quarterly or 12 for Monthly) r = Market interest rate t = No of years until maturityBond prices are typically quoted as a percentage of par value For example, assume a year corporate bond pays a 5 percent coupon rate, has a $1,000 par value and shows a price of 104Let's suppose that the face value of abond is $1,500 and the price of the bond is $1,280 while the annual coupons are$150 (apparently the rate is 10%) while the maturity period is 10 years Now ifwe put all the values in the Yield to maturity formula;


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples



Deriving The Bond Pricing Formula
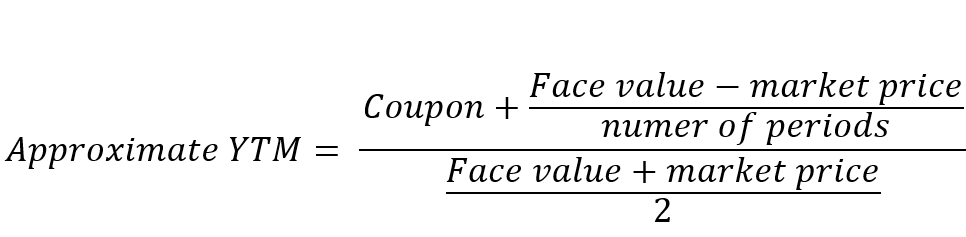
The yield to maturity formula, also known as book yield or redemption yield, is used in finance to calculate the yield of a bond at the current market price It is calculated to compare the attractiveness of investing in a bond with other investment opportunitiesIt's difficult to calculate the exact YTM, but in the formulas below we'll look at how you can calculate the approximate yield to maturity of a bond Yield to Maturity Formula YTM = \dfrac{ C \dfrac{FP}{n} }{ \dfrac{FP}{2}} C = Coupon/interest payment;F = Face value;


How To Calculate Bond Price In Excel
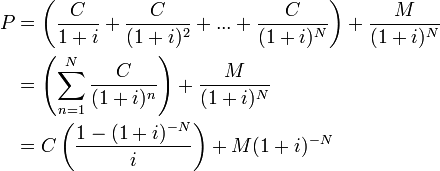


Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance
Bond Pricing Formula – Example #1 Let's calculate the price of a bond which has a par value of Rs 1000 and coupon payment is 10% and the yield is 8% The maturity of a bond is 5 years Price of bond is calculated using the formula given below Bond Price = ∑ (Cn / (1YTM)n ) P / (1i)nBecause of simple math $40 divided by $900 equates to a 45% yield You won't find the relationship this exact in real life, but this simplified example helps provide an illustration of how the process worksThe formula for calculating the yield to maturity on a zerocoupon bond is Yield To Maturity= (Face Value/Current Bond Price)^ (1/Years To Maturity)−1 Consider a $1,000 zerocoupon bond that has



Bonds Part Iii Pricing Financial Modeling History
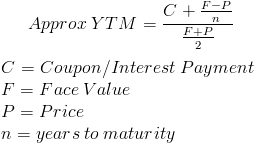


Yield To Maturity Approximate Formula With Calculator
Coupon 9% Maturity date 27 Interest paid semiannually Par Value $1000 Market price $The bond yield looks at the original price of the bond or face value The current yield differs from the yield to maturity in that the yield to maturity looks at all future inflows, including a higher or lower face value than its current price, to determine the yield based on a present value equal to the current price of the bond The formula for current yield only looks at the current price and one year coupons Example of the Current Yield FormulaNaturally, if the bond purchase price is equal to the face value, current yield will be equal to the coupon rate Current Yield= 160/2,000 = 008 or 8% Let's say the purchase price falls to 1,800 Current Yield= 160/1,800= 00 or % Current Yield rises if the purchase price falls YTM Formula The formula to calculate YTM is



How To Use The Excel Yield Function Exceljet
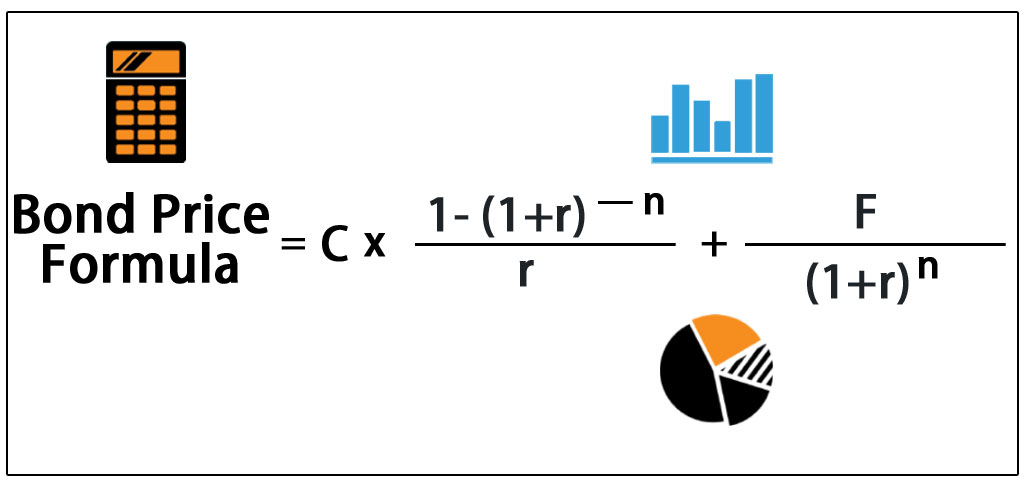


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price Examples
You will want a higher price for your bond so that yield to maturity from your bond will be 45% Let's calculate now your bond price with the same Excel PV function =PV (450%/4, 4*10, 1500, 100,000) = $112,Yield to Maturity = 429 % CALCULATE CALCULATEMaturity = Maturity date;



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds
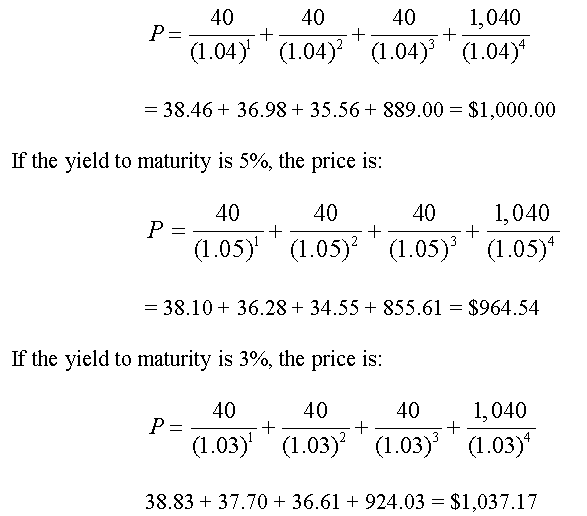


An Introduction To Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Pricing
IF c r AND Bond price < F then the bond should be selling at a discount Example of a result Let's assume that someone holds for a period of 10 years a bond with a face value of $100,000, with a coupon rate of 7% compounded semiannually, while similar bonds on the market offer a rate of return of 65%YTM = Yield(settlement, maturity, rate, price, redemption, frequency, basis) All dates are expressed either as quotes or as cell references (eg, "1/5/13", A1) Settlement = Settlement date;Because the coupon or interest rate always stays the same, the bond's price must fall to $900 to keep Bond A's yield the same as Bond B Why?
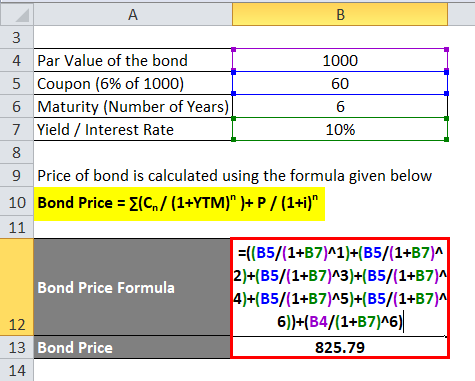


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price



Bond Valuation And Bond Yields P4 Advanced Financial Management Acca Qualification Students Acca Global
In this case, you will not want to sell your bond at 6% YTM You will want a higher price for your bond so that yield to maturity from your bond will be 45% Let's calculate now your bond price with the same Excel PV function =PV (450%/4, 4*10, 1500, 100,000) = $112,Mathematically, it the price of a coupon bond is represented as follows, Coupon Bond = ∑i=1n C/ (1YTM)i P/ (1YTM)n Coupon Bond = C * 1 (1YTM)n/YTM P/ (1YTM)n where C = Periodic coupon payment, P = Par value of bond, YTM = Yield to maturity n = No of periods till maturityBond Pricing Bond Pricing Bond pricing is the science of calculating a bond's issue price based on the coupon, par value, yield and term to maturity Bond pricing allows investors;
/DurationandConvexitytoMeasureBondRisk2-0429456c85984ad3b220cd23a760cda5.png)


Duration And Convexity To Measure Bond Risk
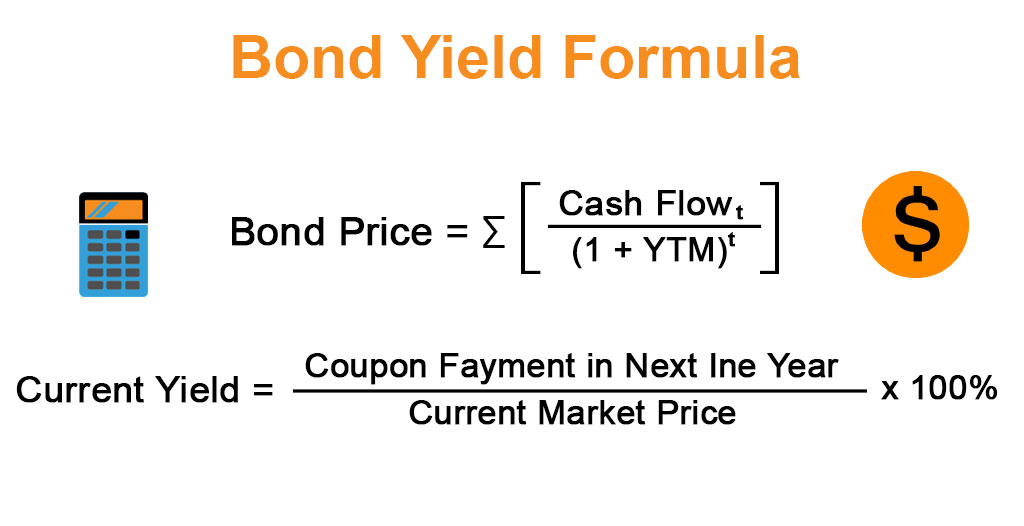


Bond Yield Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template
A bond's yield is the return an investor realizes on a bond in percentage terms If a bond pays more than one cash flow (coupon), then there is no direct formula which can be used to calculate the bond's yield Instead, an iterative approach is used This is referred to as the yield to maturity (YTM)Mathematically, the formula for bond price using YTM is represented as, Bond Price = ∑ Cash flowt / (1YTM)t Where, t No of Years to Maturity On the other hand, the term "current yield" means the current rate of return of the bond investment computed on the basis of the coupon payment expected in the next one year and the current market price The formula for current yield is expressed as expected coupon payment of the bond in the next one year divided by its current market price
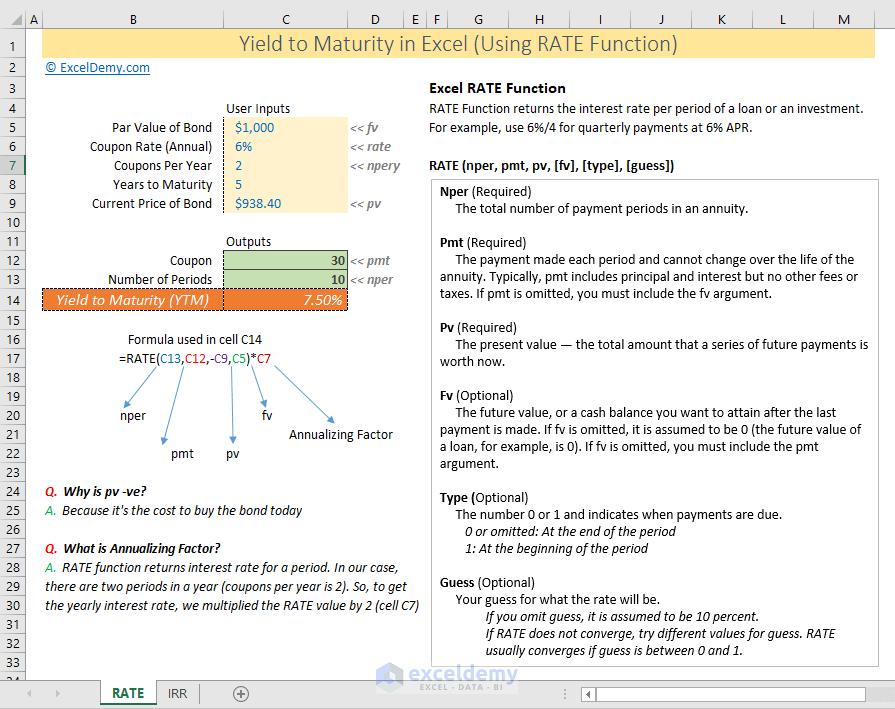


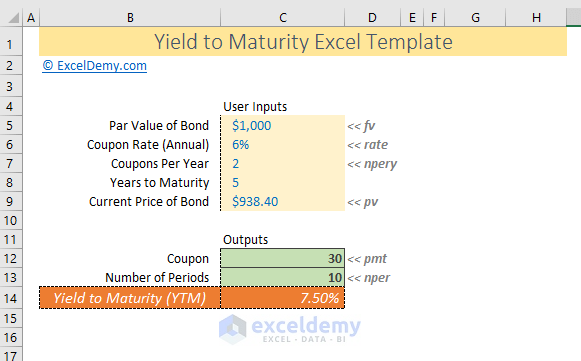
How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy
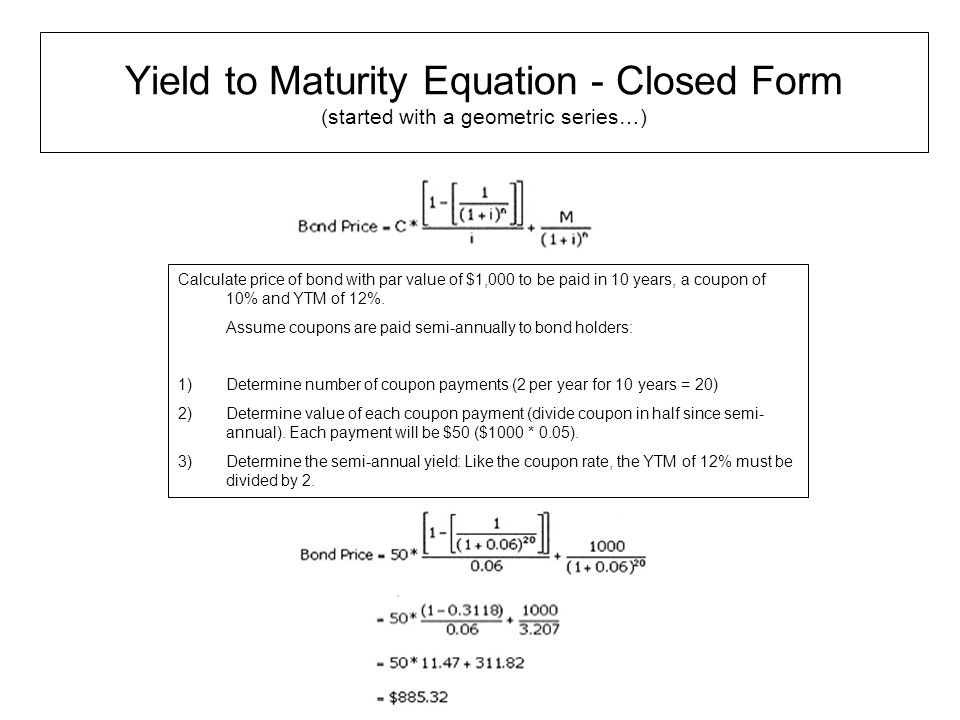


Yield To Maturity Formula Ppt Download



Interest Rate Risk Of Bonds Full Valuation Approach Aka Scenario Analysis
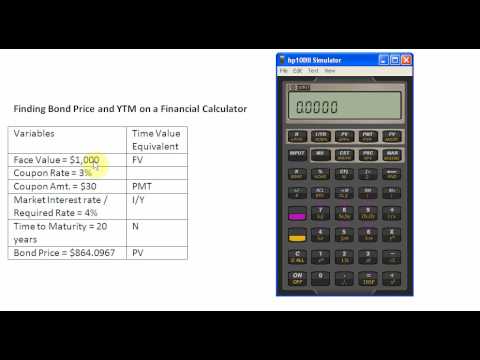


Finding Bond Price And Ytm On A Financial Calculator Youtube


Quick Guide On Bond Prices And Formula Bond Calculator Pricing Market Consensus


Understanding Bond Prices And Yields
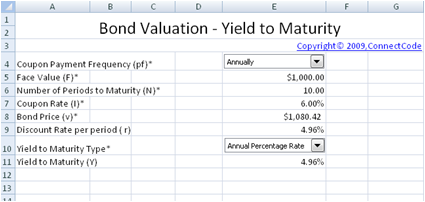


Free Bond Valuation Yield To Maturity Spreadsheet



Zero Coupon Bond Value Formula With Calculator



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures
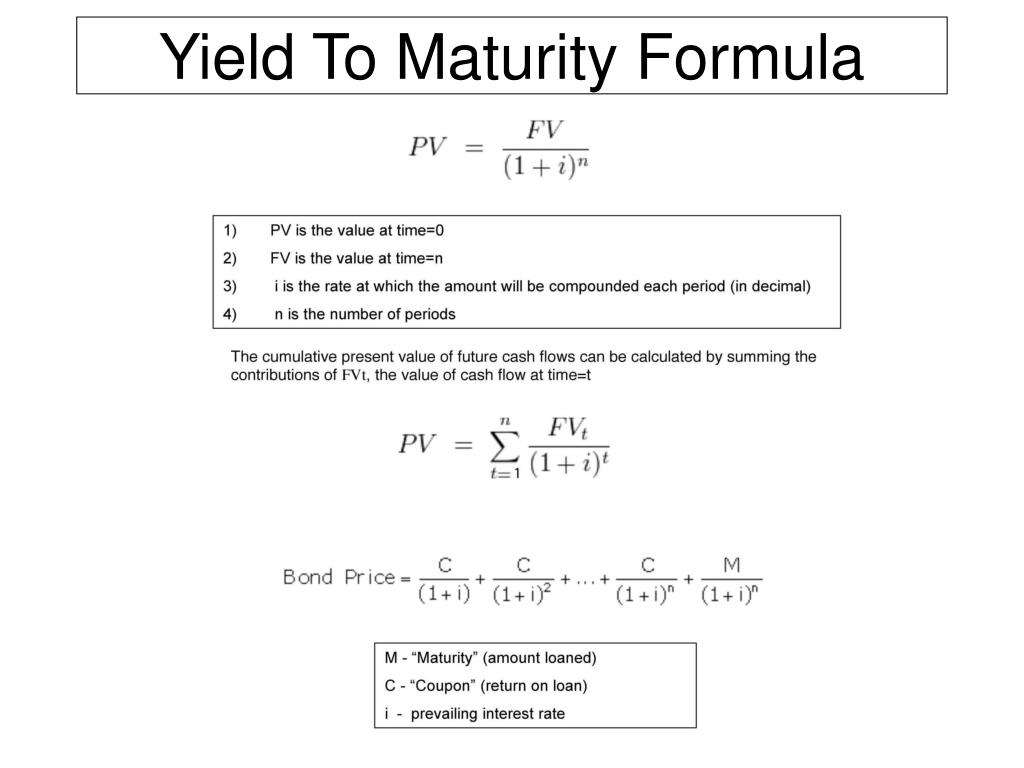


Ppt Yield To Maturity Formula Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity


Calculating Yield To Maturity Using The Bond Price



Yield Curve Wikipedia
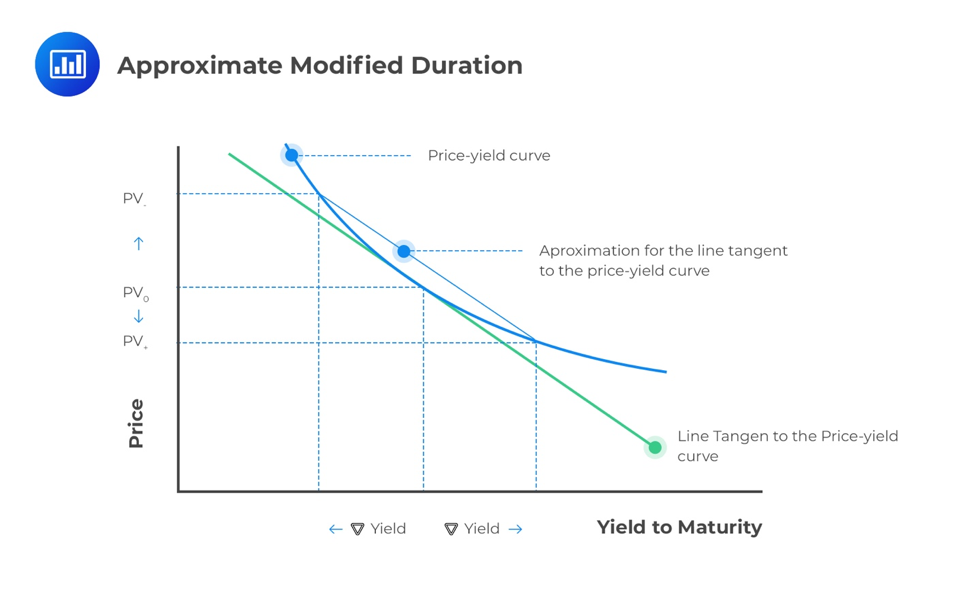


Macaulay Modified And Effective Durations Cfa Level 1 Analystprep



Yield To Maturity Fixed Income



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond


Stata Codes For Calculating Yield To Maturity For Coupon Bonds Stataprofessor



Calculate The Ytm Of A Coupon Bond Youtube
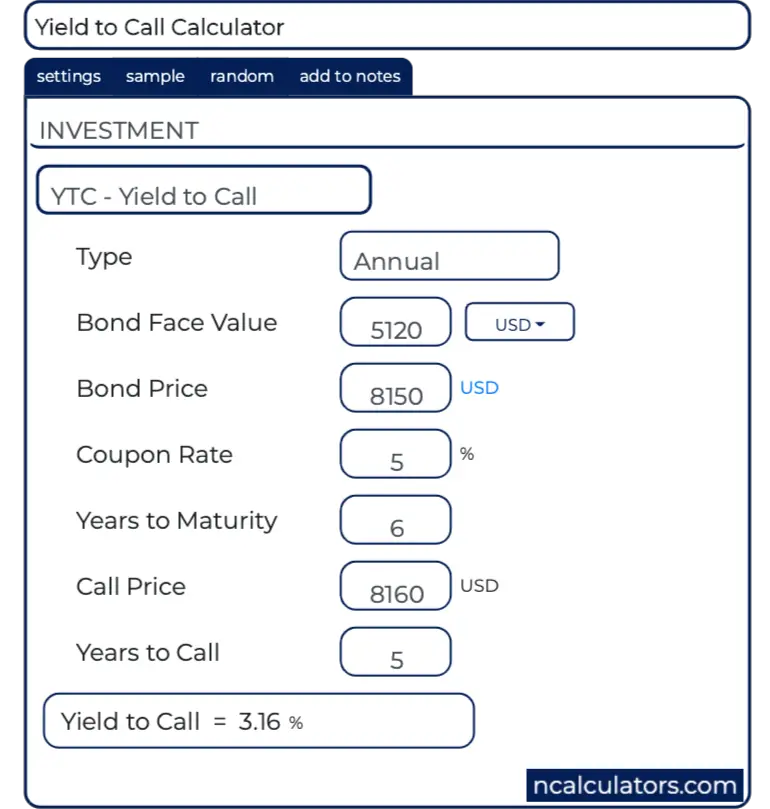


Yield To Call Ytc Calculator


Yield To Maturity Definition How To Calculate Ytm Pros Cons



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds
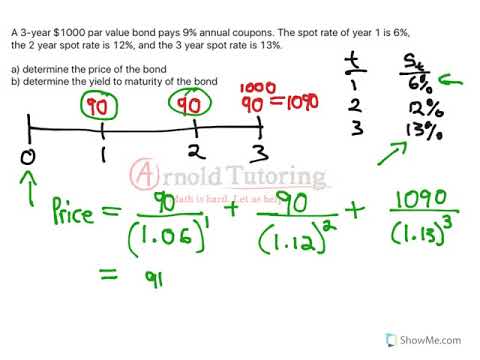


Bonds Spot Rates Vs Yield To Maturity Youtube
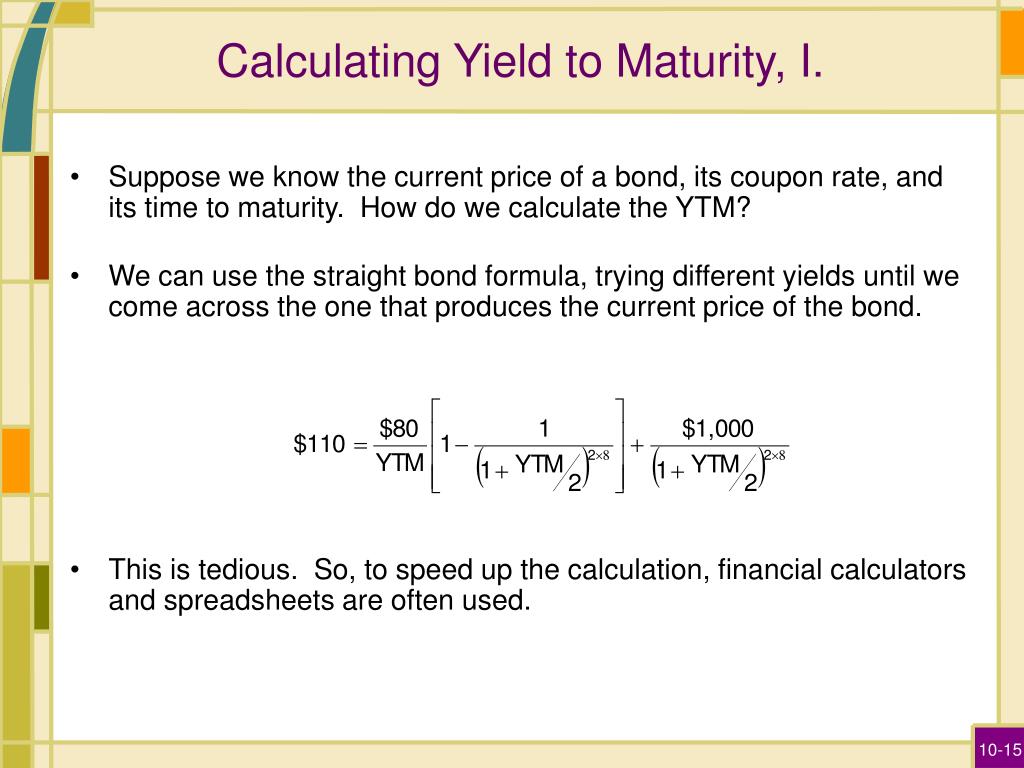


Ppt Bond Prices And Yields Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Microsoft Excel Bond Valuation Tvmcalcs Com


Coupon Rate Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing
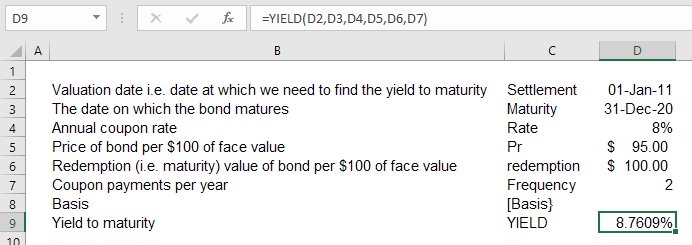


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula And Example



Best Excel Tutorial How To Calculate Yield In Excel
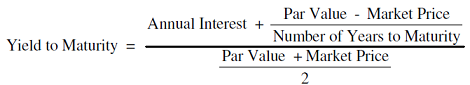


What Is Yield And How Does It Differ From Coupon Rate


Yield Curve How Yield Curve Changes Affect Annuities



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com
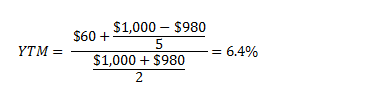


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance



Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance



Bond Basics Bond Yields Flashcards Quizlet
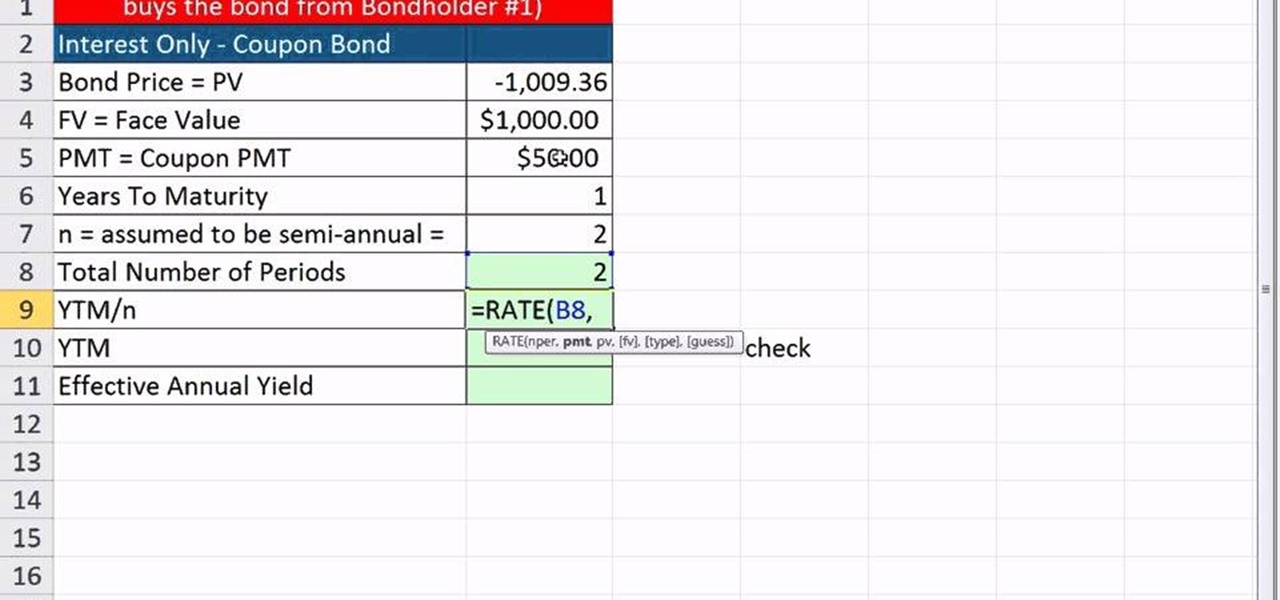


How To Calculate Ytm And Effective Annual Yield From Bond Cash Flows In Excel Microsoft Office Wonderhowto
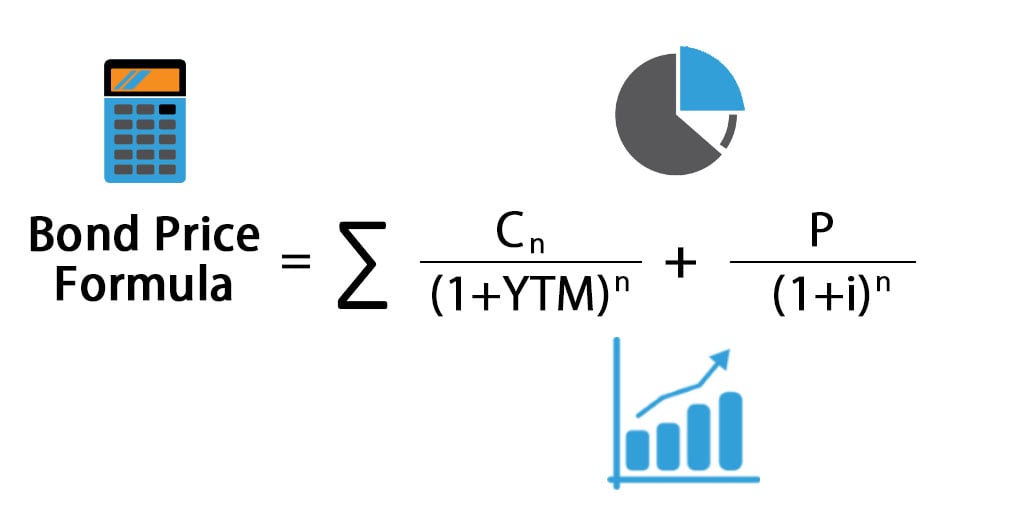


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price



Yield To Maturity Ytm And Yield To Call Ytc alectures Com



Bond Valuation Wikipedia
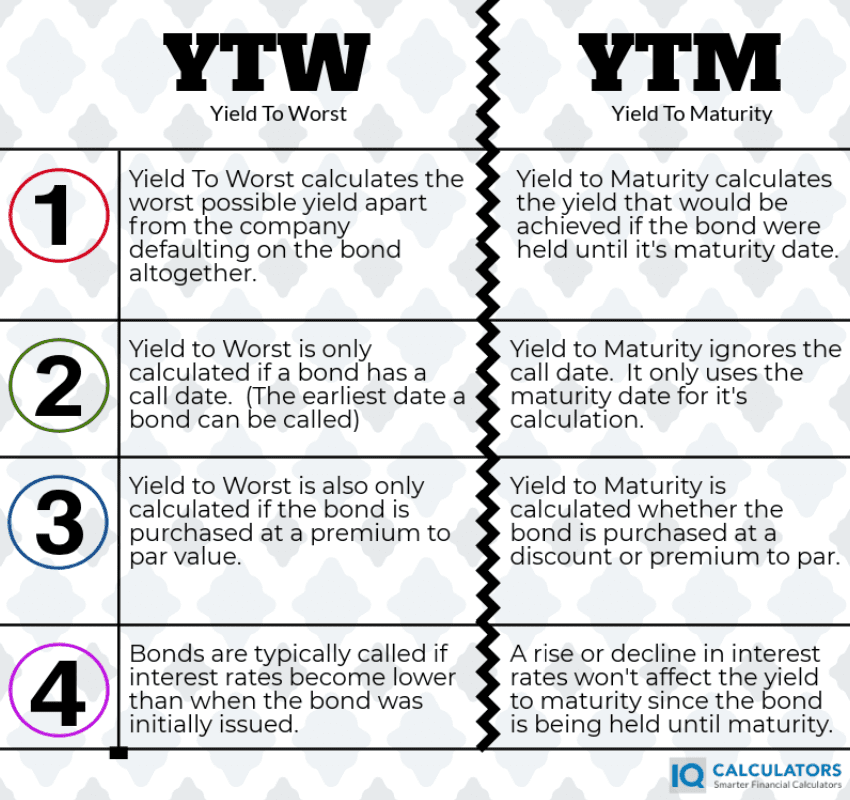


Yield To Worst What It Is And Why It S Important



Solved Page 7 Of 8 14 Points Bond Prices And Yield To M Chegg Com
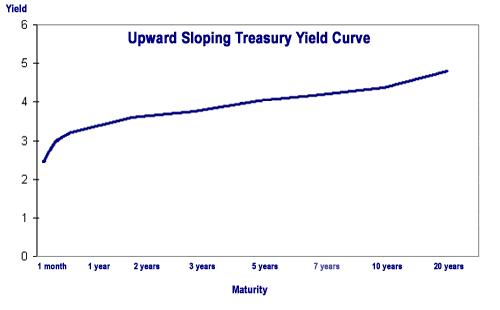


Bond Yield And Return Finra Org
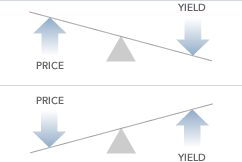


Bond Prices Rates And Yields Fidelity


Current Yield Meaning Importance Formula And More


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel



Bond Pricing And Accrued Interest Illustrated With Examples



How To Calculate The Bond Price And Yield To Maturity Youtube
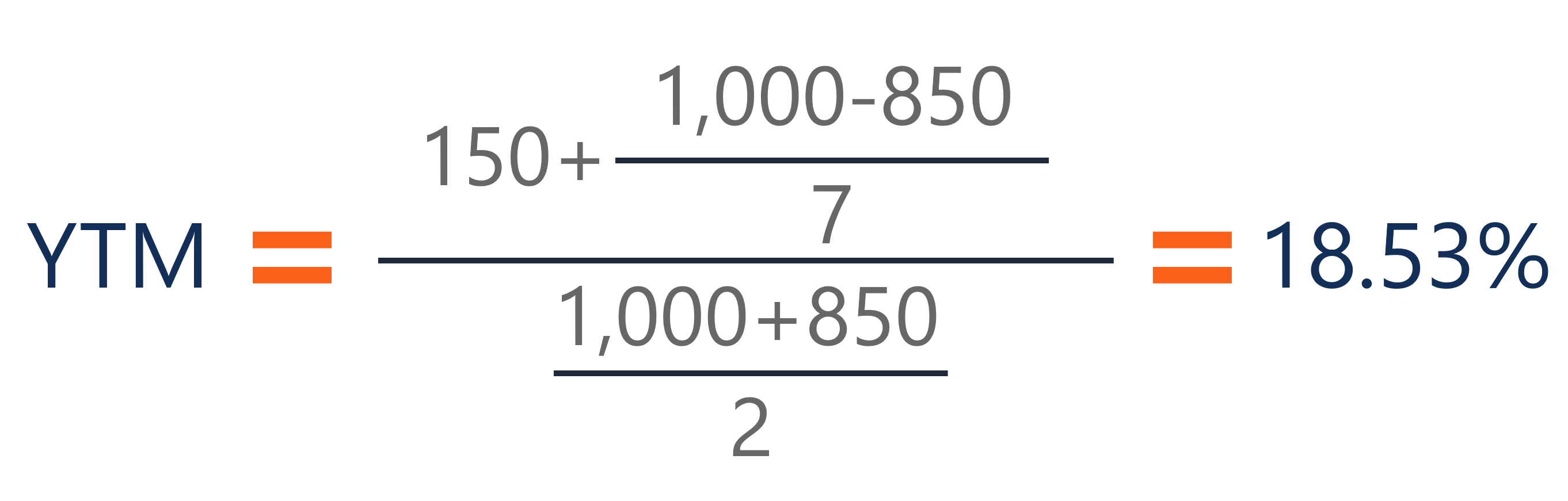


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance



Bonds Yield To Worst Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy
/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition
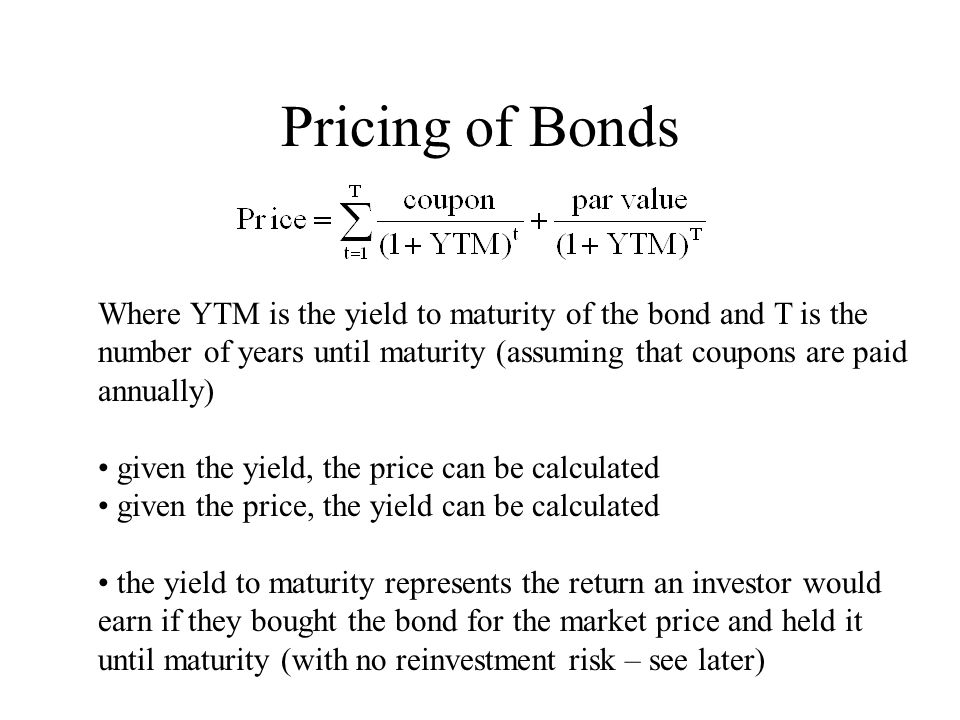


Chapter 11 Bond Yields And Prices Ppt Video Online Download
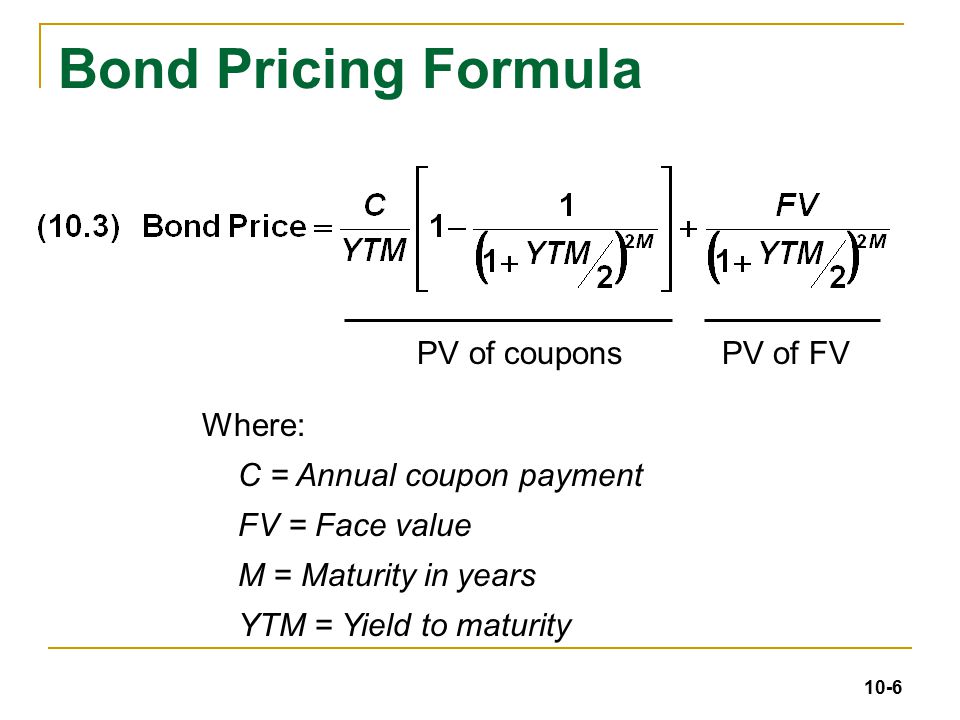


Chapter 10 Bond Prices And Yields 4 19 Ppt Download
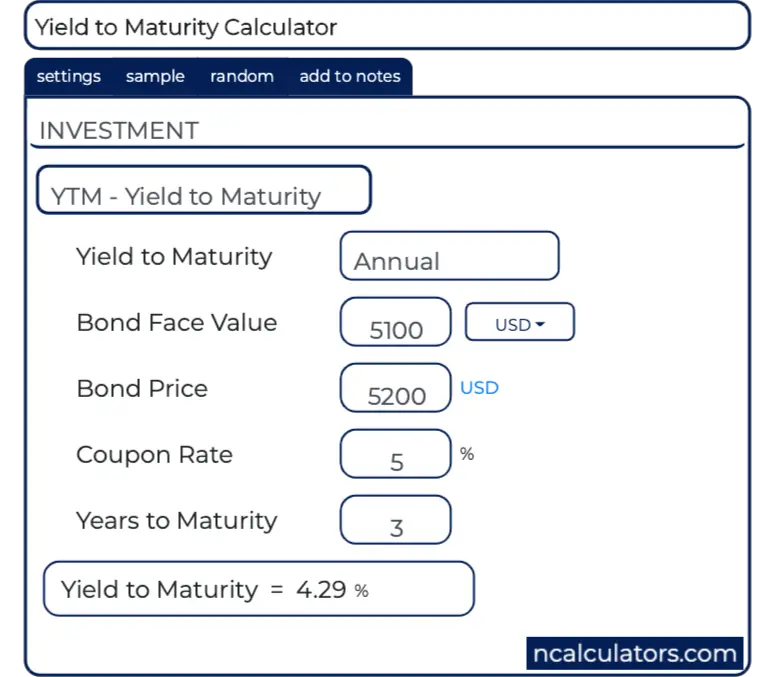


Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator
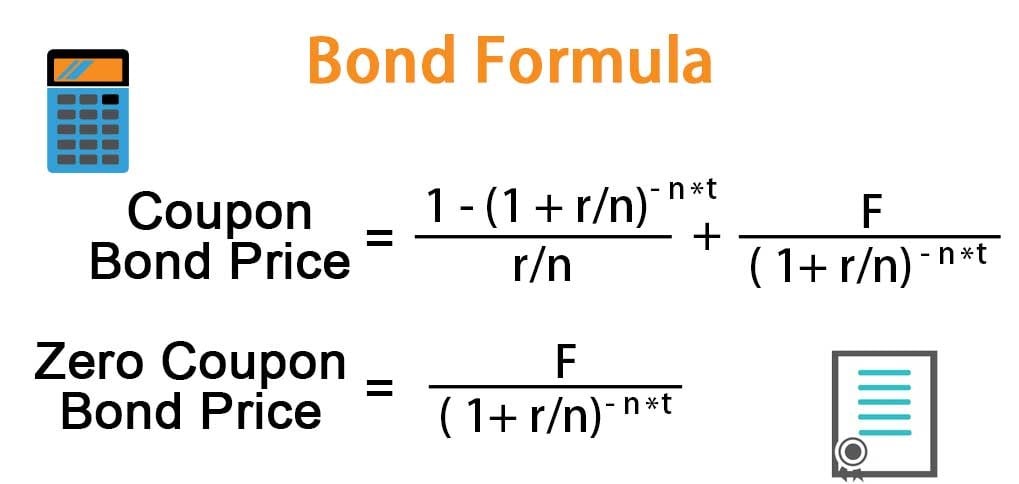


Bond Formula How To Calculate A Bond Examples With Excel Template



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



Constant Yield Price Trajectory Prepnuggets



Bond Value Calculator What It Should Be Trading At Shows Work



Quant Bonds Yield



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures
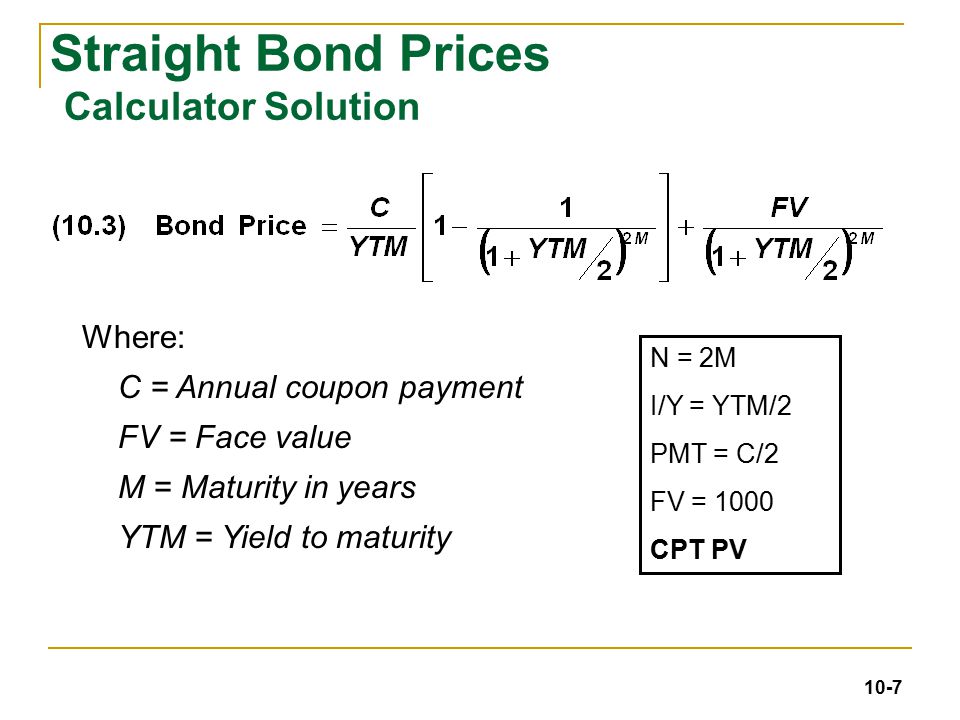


Chapter 10 Bond Prices And Yields 4 19 Ppt Download
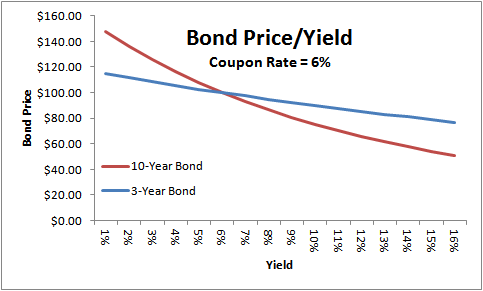


Bond Yields Nominal And Current Yield Yield To Maturity Ytm With Formulas And Examples


コメント
コメントを投稿